Prince George's County, Maryland
| Prince George's County, Maryland | ||
|
||
 Location in the state of Maryland |
||
 Maryland's location in the U.S. |
||
| Founded | 1696 | |
|---|---|---|
| Seat | Upper Marlboro | |
| Area - Total - Land - Water |
498 sq mi (1,290 km²) 485 sq mi (1,256 km²) 13 sq mi (34 km²), 2.61% |
|
| PopulationEst. - (2009) - Density |
834,560 1,709/sq mi (660/km²) |
|
| Website | www.princegeorgescountymd.gov/ | |
Prince George's County is a county located in the U.S. state of Maryland, immediately north, east, and south of Washington, D.C. As of 2009 U.S. Census Bureau estimates, it has a population of 834,560[1] and is the wealthiest county in the nation with an African-American majority.[2][3]
The county was named for Prince George of Denmark (1653–1708), the brother of King Christian V of Denmark and Norway, and husband of Queen Anne of Great Britain. It is frequently referred to as 'P.G.' or 'P.G. County,' an abbreviation which is viewed as pejorative by some residents[4].
The county is a part of the Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area. Its county seat is Upper Marlboro.
Contents |
History
Pre-history
The Cretaceous Era brought dinosaurs to the area which left a number of fossils, now preserved in a 7.5-acre (3.0 ha) park in Laurel.[5] The site, which among other finds has yielded fossilized teeth from Astrodon and Priconodon species, has been called the most prolific in the eastern United States.[6]
Post-Columbian history
Prince George's County was created by the Council of Maryland in the Province of Maryland in 1696[7] from portions of Charles and Calvert Counties and a portion was detached in 1748 to form Frederick County. Since Frederick County was subsequently divided to form the present Allegany, Garrett, Montgomery, and Washington counties, all of these counties in addition were derived from what had up to 1748 been Prince George's County.
In 1791, portions of Prince George's County were ceded to form the new District of Columbia, along with portions of Montgomery County, Maryland, as well as the parts of Northern Virginia - that were later returned to Virginia.
In April 1865, John Wilkes Booth made his escape through Prince George's County after shooting President Abraham Lincoln. He was on his way to Virginia.
On July 1, 1997, the Prince George's County section of the city of Takoma Park, Maryland, which straddled the boundary between Prince George's and Montgomery counties, was transferred to Montgomery County.[8] This was done after city residents voted to be under the sole jurisdiction of Montgomery County, and subsequent approval by both counties and the Maryland General Assembly. This was the first change in Prince George's County's boundaries since 1791, and the first alteration of the boundaries of any county in Maryland since the early 1900s.
The county has a number of properties on the National Register of Historic Places.[9]
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 498 square miles (1,290 km2). 485 sq mi (1,260 km2) of it is land and 13 sq mi (34 km2) of it (2.61%) is water.
The Patuxent River forms the county's eastern border with Howard, Anne Arundel, and Calvert Counties.
Regions
County terrain, culture and demographics differ significantly by location within the county. There are six key regions to Prince George's County, each very different: North County, East County, Central County, the Rural Tier, the Inner Beltway and South County.
Northern Prince George's County includes Laurel, Beltsville, Adelphi, College Park and Greenbelt. This area of the county is anchored by the Capitol Beltway and the Baltimore-Washington Parkway. This portion of the county is predominately white and the key employers are the University of Maryland, Beltsville Agricultural Research Center and NASA-Goddard Space Flight Center. Areas of geographic distinction include Greenbelt Park, a wooded reserve adjacent to the planned environmental community of Greenbelt and University Park a collection of historic homes adjacent to the University of Maryland. Riversdale Mansion, along with the historic homes of Berwyn Heights, Mt. Rainier and Hyattsville are also located in this area. The hidden Lake Artemesia, a park constructed during the completion of the Washington Metro Green Line, incorporates a stocked fishing lake and serves as the trail-head for an extensive Anacostia Tributary Trails system that runs along the Anacostia River and its tributaries.
Bowie, located in eastern Prince George's County is best known as a planned Levittown. William Levitt built traditional homes, as well as California contemporaries along U.S. Route 50, the key highway to the eastern shore and the state capitol of Annapolis. Bowie has currently grown to be the largest city in Prince George's County, with over 50,000 people and is also predominately white (68% [10], reflecting Levitt's initial reluctance to sell to blacks. Housing styles vary from the most contemporary to century old homes in Bowie's antique district (formerly known as Huntingtown), where the town of Bowie actually began as a haven for thoroughbred horse racing. Areas of geographic distinction include portions of the Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, the Ogden Bowie Mansion, Allen Pond, key segments of the Washington, Baltimore and Annapolis Trail, as well as planned parks, lakes and walking trails. Other communities in this section of the county are Glenn Dale and Lanham.
Central County located on the outskirts of the Capital Beltway, consists of Mitchellville, Woodmore, Greater Upper Marlboro, Springdale, Bowie and further towards the southern part of the county along the Potomac River Fort Washington. Mitchellville is named for a wealthy black family, the Mitchells, who owned a large portion of land in this area of the county. Central Avenue, a major exit off the I-95 beltway, running east to west, is one of two main roads in this portion of the county. The other major road way is Old Crain Highway, which runs north to south along the eastern portion of the county. The Newton White Mansion on the grounds is a popular site for weddings and political events.
Prince George's rural tier may be found in the area well beyond the Beltway bounded on the north by U.S. Route 50, the southwest by the Potomac River and the east by the Patuxent River. Prince George's origins are in this part of the county. Most of this area contains the unincorporated parishes, villages and lost towns of Prince George's County. Largely under postal designations of "Upper Marlboro" or "Brandywine", in truth the town of Upper Marlboro is more central county in character, though it is the post office location for various rural settlements. (The names of these unincorporated areas are listed below in the towns section of this article). Since 1721 Upper Marlboro has been the county seat of government, with families that trace their lineage back to Prince George's initial land grants and earliest governing officials. Names like Clagett, Sasscer, King James and Queen Anne pepper the streets. Street names are essentially a who's who of historical white elite and their establishments within the county.
The rural tier has been the focus of orchestrated efforts by residents and county government to preserve the rural character and environmental integrity of the rural tier. Under the Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission (M-NCPPC), Patuxent River Park is the largest natural preserve and provides public access for birdwatching and viewing the rural tier's natural waterfront vistas. In season, the park's Jug Bay Natural Area and the Patuxent Riverkeeper in Queen Anne both offer canoeing and kayaking rentals on the Patuxent. The county's largest collection of tobacco planter mansions and preserved homes are in the rural tier, some managed by the M-NCPPC. Many rural tier roads have scenic highway preservation status; a fall drive yields exceptional beauty along the Patuxent valley's Leeland Road, Croom Road, Clagett's Landing Rd., Mill Branch Rd., Queen Anne Rd., and Brandywine Rd. Most property along the roads remains in private ownership, so walking access is extremely limited except for the widespread M-NCPPC lands and trails and state holdings in the Patuxent valley such as Merkle Wildlife Sanctuary and Rosaryville State Park, both popular among hikers and mountain bikers.
The inner beltway communities of Capitol Heights, District Heights, Forestville, Suitland and Seat Pleasant border the neighboring District of Columbia's southeastern and northeastern quadrants. Some of these communities face major challenges in reducing crime.
South County has become one of the fastest growing areas of the county. Communities of Clinton, Oxon Hill, Temple Hills and Fort Washington are the largest areas of south county. The area is a mixture of the greenery of the rural tier and the new development of central county. It is the only portion of Prince George's County to enjoy Potomac River waterfront, and that geographic distinction has yielded the rise of the National Harbor project: a town center and riverside shopping and living development on the Potomac. National Harbor has become a major tourist and convention attraction, with significant hotel accommodations, eateries and shopping. Ferry rides allow trips across the Potomac into Alexandria. Several historic sites, including Mt. Vernon, can be viewed from the harbor front. River Road in Fort Washington also yields great views of the Potomac. Fort Washington Park was a major battery and gives access to the public for tours of the fort, scenic access to the river and other picnic grounds. Oxon Hill Manor offers a working farm and plantation mansion for touring; His Lordship's Kindness is another major historic home.
Adjacent jurisdictions
- Anne Arundel County (east)
- Calvert County (southeast)
- Charles County (south)
- Howard County (north)
- Montgomery County (northwest)
- Prince George's and Montgomery Counties share a bi-county planning and parks agency in the M-NCPPC and a public bi-county water and sewer utility in the Washington Suburban Sanitary Commission
- Fairfax County, Virginia (southwest)
- Alexandria, Virginia (southwest)
- Washington, DC (west)
See also: List of counties bordering eight counties
Federally protected areas
- Fort Washington Park
- Greenbelt Park
- Patuxent Wildlife Research Refuge (part)
- Piscataway Park
Government
| Year | Republican | Democrat |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 10.3% 34,246 | 89.1% 297,654 |
| 2004 | 17.4% 55,532 | 81.8% 260,532 |
| 2000 | 18.4% 49,987 | 79.5% 216,119 |
| 1996 | 21.9% 52,697 | 73.5% 176,612 |
| 1992 | 24.5% 62,955 | 65.7% 168,691 |
| 1988 | 38.8% 86,545 | 60.0% 133,816 |
| 1984 | 41.0% 95,121 | 58.6% 136,063 |
| 1980 | 40.7% 78,977 | 50.9% 98,757 |
| 1976 | 42.0% 81,027 | 58.0% 111,743 |
| 1972 | 58.5% 116,166 | 40.3% 79,914 |
| 1968 | 41.2% 73,269 | 40.3% 71,524 |
| 1964 | 36.2% 46,413 | 63.8% 81,806 |
| 1960 | 42.0% 44,817 | 58.0% 62,013 |
Since 1792, the county seat has been Upper Marlboro. Prior to 1792, the county seat was located at Mount Calvert, a 76 acre (308,000 m²) estate along the Patuxent River on the edge of what is now in the unincorporated community of Croom.
Prince George's County has become a stronghold for Democrats running in the state.
Prince George's County was granted a charter form of government in 1970 with the county executive elected as the head of the executive branch and the county council members as the leadership of the legislative branch. Prince George's County is part of the Seventh Judicial Circuit of the state of Maryland and holds 23 of the 32 total circuit court judges in the circuit (which incudes Calvert, Charles, Prince George's, and St. Mary's counties).[11]
County executive
| Name | Party | Term |
|---|---|---|
| William W. Gullett | Republican | 1970–1974 |
| Win Kelly | Democrat | 1974–1978 |
| Lawrence Hogan | Republican | 1978–1982 |
| Parris N. Glendening | Democrat | 1982–1994 |
| Wayne K. Curry | Democrat | 1994–2002 |
| Jack B. Johnson | Democrat | 2002–present |
Other officials
- State's Attorney: Glenn F. Ivey
- County Sheriff: Michael A. Jackson
- Chief of the County Police: Roberto Hylton
- Superintendent of schools: Dr. William R. Hite
State and national representation
The county is represented in the United States House of Representatives by Steny Hoyer (5th District) who was elected House Majority Leader in 2007, Donna Edwards (4th District), and Chris Van Hollen (8th District).
At the state level, the county is represented in the Maryland Senate and the Maryland House of Delegates by Districts 21, 22, 23 (A and B), 24, 25, 26, 27A, and 47 (23 delegates and 8 senators total).
Demographics
| Historical populations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1900 | 29,898 |
|
|
| 1910 | 36,147 | 20.9% | |
| 1920 | 43,347 | 19.9% | |
| 1930 | 60,095 | 38.6% | |
| 1940 | 89,490 | 48.9% | |
| 1950 | 194,182 | 117.0% | |
| 1960 | 357,395 | 84.1% | |
| 1970 | 660,567 | 84.8% | |
| 1980 | 665,071 | 0.7% | |
| 1990 | 729,268 | 9.7% | |
| 2000 | 801,515 | 9.9% | |
| Est. 2007 | 828,770 | 3.4% | |
As of the estimated American Community Survey Census of 2008, there were 825,924 people, 298,439 households, and 198,047 families residing in the county.[12] The population density was 1,651/sq mi (638/km²). There were 308,929 housing units at an average density of 623/sq mi (241/km²).
The racial makeup of the county was:
- 62.70% African American
- 27.04% White
- 7.12% Hispanic or Latino
- 3.87% Asian
- 3.38% Other races
- 2.61% Two or More of any race
- 0.35% Native American
- 0.06% Pacific Islander
There were 298,439 households out of which 65.1% are family households and 34.9% were non-family households.[13]. 36.4% of households had children under the age of 18 living with them, 44.00% were married couples living together, 19.60% had a female householder with no husband present. 24.10% of all households were made up of individuals and 4.90% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.74 persons and the average family size was 3.25 persons.
In the county the population was spread out with 26.80% under the age of 18, 10.40% from 18 to 24, 33.00% from 25 to 44, 22.10% from 45 to 64, and 7.70% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33 years. For every 100 females there were 91.50 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 87.20 males.
The median income for a household in the county in 2008 was $71,696,[14] and the median income for a family was $81,908; The 2008 mean income for a family in the county was $94,360. As of 2000 Males had a median income of $38,904 versus $35,718 for females. The 2008 per capita income for the county was $23,360. About 4.70% of families and 7.40% of the population were below the poverty line, including 9.2% of those under age 18 and 7.1% of those age 65 or over. Prince George's County is the 70th most affluent county in the United States by median income for families and the most affluent county in the United States with an African-American majority. Almost 38.8% of all households in Prince Georges County, earned over $100,000 in 2008.[15]
Education Attainment
30.1% of all residents over the age of 25 had graduated from college and obtained a bachelors degree (17.8%)or professional degree (12.2%)[13]. 86.2% of all residents over the age of 25 were high school graduates or higher.
Crime
Prince George’s County accounted for 20% of murders in the state of Maryland from 1985 to 2006.[16] A twenty year crime index trends study performed by Prince George's County Police Department Information Resource Management, showed the county had a 23.1% increase in total crime for the years of 2000 to 2004. Between the years of 1984 to 2004, Prince George’s had a 62.8% increase in total crime.[17]
However, as of 2009, crime has generally declined in the county [18] and the number of homicides has declined from 151 in 2005 to 99 in 2009.[19][20]
Religion
The county is home to over 800 churches, as well as a number of mosques, synagogues, and Hindu temples. Property belonging to religious entities makes up 3,450 acres (14.0 km2) of land in the county.[21]
Emergency services
Law enforcement

Prince George's County is serviced by multiple law enforcement agencies. The Prince George's County Police Department is the primary police service for county residents residing in unincorporated areas of the county. In addition, the Prince George's County Sheriff's Office acts as the enforcement arm of the county court, and also shares some patrol responsibility with the county police. County parks are serviced by the Prince George's County Division of the Maryland-National Capital Park Police. Besides the county-level services, all but one of the 27 local municipalities maintain police departments that share jurisdiction with the county police services. Furthermore, the Maryland State Police enforces the law on state highways which pass through the county and the Maryland Department of Natural Resources Police patrol the state parks and navigable waterways located within the county.
Along with the state and local-level law enforcement agencies, the federal government also maintains several departments that service citizens of the county such as the US Park Police, US Postal Police, Andrews Air Force Base Security Police, and other federal police located on various federal property located within the county.
In addition, nearly all of the incorporated cities and towns in the county have their own municipal police force. Notable exceptions include the city of College Park.
As of 2006, the county reportedly contains the highest crime rate for the Washington Metro area, comparable to Baltimore.[22][23]
Emergency medical and fire services
Prince George's County hospitals include Bowie Health Center, Doctors Community Hospital in Lanham, Gladys Spellman Specialty Hospital & Nursing Center in Cheverly, Hospice of the Chesapeake in Landover, Laurel Regional Hospital in Laurel, Prince George's Hospital Medical Center in Cheverly, and Southern Maryland Hospital Center in Clinton.[24] Fort Washington Medical Center also provides a small medical facility for its community.[25]
The Prince George's County Volunteer Firemen's Association was formed in 1922 with several of the first companies organized in the county. The first members of the association were Hyattsville, Cottage City, Mount Rainier, and Brentwood.
In March 1966, the Prince George's County Government employed the firefighters who had been hired by individual volunteer stations and an organized career department was begun. The career firefighters and paramedics are represented by IAFF 1619.
Prince George's County became the first jurisdiction in Maryland to implement the 9-1-1 Emergency Reporting System in 1973. Advanced life support services began for citizens of the county in 1977. Firefighters were certified as Cardiac Rescue Technicians and deployed in what was called at the time Mobile Intensive Care Units to fire stations in Brentwood, Silver Hill, and Laurel.
As of 2007, the Prince George's County Fire/EMS Department operates a combination system staffed by over 800 career firefighters and paramedics, and nearly 1,100 active volunteers.
Education
Colleges and universities
- Bowie State University, located in unincorporated area north of Bowie
- Capitol College, located in unincorporated area south of Laurel
- Prince George's Community College, located in unincorporated area (Largo)
- Strayer University, PG Campus, in unincorporated area (Suitland)
- TESST College of Technology, located in unincorporated area (Beltsville)
- University of Maryland, College Park, in College Park
- University of Maryland University College, in unincorporated area (Adelphi)
- Washington Bible College and Capital Bible Seminary, in unincorporated area (Lanham)
Public schools
The county's schools are managed by the Prince George's County Public Schools system.
Transportation
The County contains a large portion of the Capital Beltway. After a decades-long debate, construction began in late 2007 on an east-west toll freeway, the Intercounty Connector ("ICC"), which will extend Interstate 370 in Montgomery County in order to connect I-270 with Interstate 95 and U.S. 1 in Laurel. The ICC is expected to be complete in 2012.
The Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority operates Metrobus fixed-route buses and Metrorail heavy-rail passenger service in and out of the County as well as the regional Metro Access paratransit system for the handicapped. Prince George's County Department of Public Works and Transportation also operates The Bus, a county-wide fixed-route bus system, and the "Call-A-Ride" on-request bus service for passengers who are distant from a bus stop or have difficulty using bus service. Call-A-Ride is an on-request service which generally requires 3-days advance reservations. The county also offers a subsidized taxicab service for the elderly and handicapped called "Call-A-Cab" in which eligible customers who sign up for the service purchase coupons giving them a 50% discount with participating taxicab companies in Prince George's and Montgomery Counties.
Fifteen stations of the Washington Metro subway system are located in Prince George's County, with four of them as terminus stations: Greenbelt, New Carrollton, Largo, and Branch Avenue. There has been much debate on the construction of the Purple Line, which would link highly-developed areas of both Montgomery and Prince George's Counties. Also worth noting is the potential expansion of the Green Line northward to Laurel and beyond.
The MARC Train (Maryland Area Rail Commuter) train service has two lines that traverse Prince George's County. The Camden Line runs between Baltimore Camden Station and Washington Union Station and has six stops in the county in Riverdale Park, College Park, Greenbelt, Muirkirk, Laurel and Laurel Racetrack. The Penn Line runs on the AMTRAK route between Baltimore Penn Station and Washington Union Station. It has three stops in the county: Bowie State, Seabrook, and New Carrollton.
The College Park Airport (est. 1909) is the world's oldest continuously operated airport, and has adjacent historical museum and an early aviation-themed restaurant.
Residents may use Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport in Arlington County, Virginia, Baltimore-Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport near Baltimore, and Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia.
Major highways
 Interstate 95 enters the county at Laurel. It joins with Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway) in College Park where it continues and leaves at the Woodrow Wilson Bridge over the Potomac River.
Interstate 95 enters the county at Laurel. It joins with Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway) in College Park where it continues and leaves at the Woodrow Wilson Bridge over the Potomac River. Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway) enters the county near Adelphi, and joins Interstate 95 at the College Park Interchange here it continues and leaves at the Woodrow Wilson Bridge over the Potomac River.
Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway) enters the county near Adelphi, and joins Interstate 95 at the College Park Interchange here it continues and leaves at the Woodrow Wilson Bridge over the Potomac River. U.S. 1 is a major north-south roadway running through the county, entering the county at Laurel and leaving at the state border with Washington, D.C. at Mount Rainier.
U.S. 1 is a major north-south roadway running through the county, entering the county at Laurel and leaving at the state border with Washington, D.C. at Mount Rainier. US 50 is a major limited-access highway that spans the county from east to west, entering at Cheverly and exiting at Bowie. This highway is also Interstate 595 but there are no signs. However, the reconstruction of this highway was funded as an Interstate highway: 90% Federal funds and 10% Maryland funds.
US 50 is a major limited-access highway that spans the county from east to west, entering at Cheverly and exiting at Bowie. This highway is also Interstate 595 but there are no signs. However, the reconstruction of this highway was funded as an Interstate highway: 90% Federal funds and 10% Maryland funds.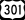 US 301 also called Crain Highway, is a major divided roadway, entering with MD 5 near Brandywine, and continuing north where it intersects with US 50 and turns into Route 3.
US 301 also called Crain Highway, is a major divided roadway, entering with MD 5 near Brandywine, and continuing north where it intersects with US 50 and turns into Route 3.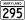 State Route 295 is the hidden designation for the portion of the Baltimore-Washington Parkway that runs north-south through the county. It runs from the intersection of Route 50 and MD 201 at the DC/MD line, and continues into Anne Arundel County to Baltimore.
State Route 295 is the hidden designation for the portion of the Baltimore-Washington Parkway that runs north-south through the county. It runs from the intersection of Route 50 and MD 201 at the DC/MD line, and continues into Anne Arundel County to Baltimore. also called Pennsylvania Avenue, runs from the Maryland-DC border eastward into Anne Arundel County and south in Calvert County.
also called Pennsylvania Avenue, runs from the Maryland-DC border eastward into Anne Arundel County and south in Calvert County. also called Branch Avenue, runs from Maryland-DC border southeast through Charles County into St. Mary's County.
also called Branch Avenue, runs from Maryland-DC border southeast through Charles County into St. Mary's County. also called Central Avenue, runs from Capitol Heights eastward through the center of the county, through Bowie, and into Anne Arundel County.
also called Central Avenue, runs from Capitol Heights eastward through the center of the county, through Bowie, and into Anne Arundel County. also called Landover Road (north of 214) and Largo Road (south of 214), runs northward from the town of Upper Marlboro to Hyattsville.
also called Landover Road (north of 214) and Largo Road (south of 214), runs northward from the town of Upper Marlboro to Hyattsville.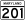 also called Kenilworth Avenue, runs north from the Maryland-DC border in Cheverly. After the intersection with Cherrywood Lane in Greenbelt, the name changes to Edmonston Road, which continues north until it ends in Laurel.
also called Kenilworth Avenue, runs north from the Maryland-DC border in Cheverly. After the intersection with Cherrywood Lane in Greenbelt, the name changes to Edmonston Road, which continues north until it ends in Laurel.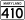 also known as East-West Highway, stretches from the Prince George's County-Montgomery County border near Takoma Park to its end in Landover. In the town of Riverdale Park, it is called Riverdale Road.
also known as East-West Highway, stretches from the Prince George's County-Montgomery County border near Takoma Park to its end in Landover. In the town of Riverdale Park, it is called Riverdale Road. also called Annapolis Road, runs laterally from Hyattsville to Route 3 in Bowie.
also called Annapolis Road, runs laterally from Hyattsville to Route 3 in Bowie.
 also called the Intercounty Connector (ICC) (Maryland Route 200), a long-planned toll road, is under construction as of late 2007,[26] and will run west from U.S. 1 just south of Laurel, crossing Virginia Manor Road, with a major new interchange at Interstate 95; then continuing west into Montgomery County and interchanging with U.S. 29, Maryland Route 97 (Georgia Avenue) and terminating at Interstate 370 near Shady Grove, Rockville and Gaithersburg, and providing a direct freeway connection to Interstate 270 via Interstate 370.
also called the Intercounty Connector (ICC) (Maryland Route 200), a long-planned toll road, is under construction as of late 2007,[26] and will run west from U.S. 1 just south of Laurel, crossing Virginia Manor Road, with a major new interchange at Interstate 95; then continuing west into Montgomery County and interchanging with U.S. 29, Maryland Route 97 (Georgia Avenue) and terminating at Interstate 370 near Shady Grove, Rockville and Gaithersburg, and providing a direct freeway connection to Interstate 270 via Interstate 370.
Enterprises and recreation
Prince George's County is home to the United States Department of Agriculture's Henry A. Wallace Beltsville Agricultural Research Center, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, the United States Census Bureau, Andrews Air Force Base, the National Archives and Records Administration's College Park facility, the University of Maryland's flagship College Park campus, Six Flags America and Six Flags Hurricane Harbor, FedEx Field (home of the Washington Redskins), and the National Harbor, which its developers, Peterson Companies and Gaylord Entertainment Company, bill as the largest single mixed-use project and combined convention center–hotel complex on the East Coast.
Media
- WPGC-FM, Morningside, MD, take their P-G-C call letters from the name Prince George's County.
Recreation
Although Prince George's County isn't often credited for the Washington Redskins, the Redskins stadium is in Landover. No other major-league professional sports teams are in the county, though Bowie hosts the Bowie Baysox, a minor league baseball team. The county is known for its very successful youth in basketball ESPN published an article declaring Prince Georges County the new "Hoops Hot Bed" and ranked it as the number one basketball talent pool in the country.[27]. A number of basketball prospects, including Ty Lawson, Kevin Durant, and Michael Beasley from AAU basketball teams such as the PG Jaguars, DC Assault, PG Elite Basketball and DC Blue Devils. Besides AAU, basketball has skyrocketed from local high schools such as DeMatha Catholic High School and Bishop McNamara High School, both of which have found some great success locally and nationally.
Cities and towns
This county contains the following incorporated municipalities:
| 10 Cities | 17 Towns |
|---|---|
|
|
The city of Takoma Park was formerly partly in Prince George's County, but since 1997 has been entirely in Montgomery County. The part of Takoma Park that changed counties comprises two residential neighborhoods, Carole Highlands ( part of this neighborhood is still in Prince George's County), and New Hampshire Gardens.
Unincorporated places
Unincorporated areas are also considered as towns by many people and listed in many collections of towns, but they lack local government. Various organizations, such as the United States Census Bureau, the United States Postal Service, and local chambers of commerce, define the communities they wish to recognize differently, and since they are not incorporated, their boundaries have no official status outside the organizations in question. The Census Bureau recognizes the following census-designated places in the county:
|
|
|
|
Other unincorporated places not listed as Census-Designated Places but known in the area include:
|
|
|
|
And two localities: Muirkirk (near Montpelier) and Chapel Oaks (near Fairmount Heights)
Sister cities
Prince George's County has three sister cities, as designated by Sister Cities International:
 Royal Bafokeng Nation, South Africa
Royal Bafokeng Nation, South Africa Rishon LeZion, Israel
Rishon LeZion, Israel Ziguinchor, Senegal
Ziguinchor, Senegal
Notable residents
- Chris Adler, American film actor, grew up in Greenbelt and attended Eleanor Roosevelt High School in Greenbelt.
- Dr. John Bayne, 19th-century founder of the University of Maryland, superintendent of county schools, Union Army physician, and one of the first Americans to grow and eat a tomato, proving they were not poisonous as had been thought, lived on Oxon Hill Road in Oxon Hill.
- Michael Beasley, professional basketball player for the Miami Heat.
- Len Bias, All-American Basketball star at the University of Maryland in the 1980s, grew up in Landover Hills and attended Northwestern High School in Hyattsville.
- Riddick Bowe, former world heavyweight boxing champion, and family lived in Sero Estates, Fort Washington.
- Sergey Brin, founder of Google, grew up in Adelphi and attended Eleanor Roosevelt High School in Greenbelt.
- John Carroll, S.J. (1735–1815), first Roman Catholic Bishop and Archbishop in the United States, and founder of Georgetown University, was born in Upper Marlboro.
- JC Chasez, singer/producer, grew up in Bowie, Maryland.
- Frank Cho, award-winning cartoonist, grew up in Beltsville and attended community college and university in the county.
- Thomas John Claggett (1742–1816), first Episcopal Bishop consecrated in the United States and third Chaplain of the United States Senate, was from Upper Marlboro.
- Leonard Covington (1768–1813), born in Aquasco, United States Congressman from Maryland[28]
- Kevin Durant, professional basketball player for the Oklahoma City Thunder.
- Roger Easton, Sr., Naval scientist, the chief inventor of GPS and winner of the 2004 National Medal of Technology, lived on Oxon Hill Road in Oxon Hill.
- Francis B. Francois, lawyer and engineer, lived in Bowie, Maryland for over 40 years. In 1999, he was elected to the National Academy of Engineering in recognition of his achievements in the field of engineering and policy leadership in surface transportation infrastructure and research. He served on the Prince George's County council as an elected official for 10 years.
- Steven F. Gaughan, Prince George's County Police Officer killed in the line of duty in 2005.
- Kathie Lee Gifford, network television personality, grew up in Bowie.
- Mya Harrison, pop musician, known simply as Mya.
- Goldie Hawn, actress, director, and producer, grew up in Takoma Park before it was transferred to Montgomery County.
- Jim Henson, creator of the Muppets later used on Sesame Street, grew up in University Park, Maryland and attended Northwestern High School in Hyattsville, Maryland.
- Taraji P. Henson, actress, attended Oxon Hill High School.
- Steny Hoyer, current Majority Leader of the United States House of Representatives, lived as a teenager in Suitland and Mitchellville, attended Suitland High School and Univ. Maryland - College Park, and later lived in Friendly before moving to St. Mary's County.
- Cathy Hughes, founder and manager of Radio One, the nation's largest African American broadcasting company.
- Martin Lawrence, actor and comedian, lived in Landover and attended Eleanor Roosevelt High School in Greenbelt.
- Sugar Ray Leonard, boxing champion, grew up in Palmer Park.
- G. Gordon Liddy, Presidential aide convicted in the Watergate scandal, later an author and radio personality, lives in Fort Foote, Fort Washington.
- Sammy Nestico, band music arranger, lived in Oxon Hill in the 1960s.
- Jan Scruggs, who conceived the National Vietnam Veterans Memorial, grew up in Bowie.
- Isis Tsunami, First transgender contestant in America's Next Top Model (in cycle 11).
- Sumner Welles, U.S. Undersecretary of State to Franklin Roosevelt, built and lived in Oxon Hill Manor, which is now a public facility.
- Morgan Wootten coached at DeMatha Catholic High School in Hyattsville, Maryland from 1956 to 2002. The coach with the most wins in high school basketball history, he was elected to the Basketball Hall of Fame, the only high school basketball coach ever so honored. He currently resides in University Park, Maryland.
- Wale, a hip-hop artist, who often notes in his songs how he is from "PG County," and the "DMV" region (D.C, Maryland, Virginia).
References
- ↑ "Prince George's County, Maryland." U.S. Census Bureau, 2007.
- ↑ Howell, Tom Jr. (2006-04-18). "Census 2000 Special Report. Maryland Newsline, Census: Md. Economy Supports Black-Owned Businesses". University of Maryland. Philip Merrill College of Journalism. http://www.newsline.umd.edu/business/specialreports/census/blackbusiness041806.htm.
- ↑ Chappell, Kevin (November 2006). "America's Wealthiest Black County"]. Ebony. http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1077/is_1_62/ai_n16807718. Retrieved 2007-02-14.
- ↑ Parker, Lonnae O'Neal; Wiggins, Ovetta (May 7, 2006). ""'P.G.': Insult or Abbreviation?"". Washington Post. p. C05. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/05/06/AR2006050601260.html. Retrieved 2008-05-01.
- ↑ "Dinosaur Park Officially Dedicated and Opened To the Public". pgparks.com. Prince George's County Department of Parks and Recreation. http://www.pgparks.com/About-Parks-and-Recreation/HomePage_Read_More/Dinosaur_Park_Officially_Dedicated_and_Opened_To_the_Public.htm. Retrieved October 28, 2009.
- ↑ Roylance, Frank D. (October 25, 2009). "Where dinosaurs once walked". baltimoresun.com. The Baltimore Sun. http://www.baltimoresun.com/news/maryland/bal-md.dinosaur25oct25,0,2758500.story. Retrieved October 28, 2009.
- ↑ "Proceedings of the Council of Maryland, 1696/7:1698, Volume 23, Page 23". Maryland State Archives. http://aomol.net/megafile/msa/speccol/sc2900/sc2908/000001/000023/html/am23--23.html. Retrieved 05/04/2007.
- ↑ "Substantial Changes to Counties and County Equivalent Entities: 1970-Present". Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/tiger/ctychng.html. Retrieved 8 August 2009.
- ↑ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 2008-04-15. http://www.nr.nps.gov/.
- ↑ http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/24000.html of the population)
- ↑ http://www.msa.md.gov/msa/mdmanual/31cc/html/ccf.html
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/ACSSAFFFacts?_event=Search&_lang=en&_sse=on&geo_id=05000US24033&_county=Prince+George's+County
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/ADPTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=05000US24033&-qr_name=ACS_2008_3YR_G00_DP3YR2&-ds_name=ACS_2008_3YR_G00_&-_lang=en&-redoLog=true&-_sse=on
- ↑ http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/24/24033.html
- ↑ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/ADPTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=05000US24033&-qr_name=ACS_2008_3YR_G00_DP3YR3&-ds_name=ACS_2008_3YR_G00_&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false&-_sse=on
- ↑ http://somd.com/news/headlines/2007/5809.shtml
- ↑ http://www.co.pg.md.us/Government/PublicSafety/Police/2004Statistics/12-Year_YTD_Trends.pdf
- ↑ http://www.gazette.net/stories/01142010/prinnew162102_32559.php
- ↑ http://www.princegeorgescountymd.gov/Government/PublicSafety/Police/CrimePE/pdfs/december-08-ucr-county.pdf
- ↑ http://www.princegeorgescountymd.gov/Government/PublicSafety/Police/pdfs/december06ucr_countywide.pdf
- ↑ Harris, Sudarsan; Harris, Hamil R. (March 14, 2005). Tax Exempt and Growing, Churches Worry Pr. George's. The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A32382-2005Mar13.html. Retrieved 2008-03-26]
- ↑ ""Baltimore, Prince George's Reign as State's Murder Capitals"". Southern Maryland Online. April 24, 2007. http://somd.com/news/headlines/2007/5809.shtml.
- ↑ "Maryland Uniform Crime Reporting (UCR) data: 1985 - 2006". Governor's Office of Crime Prevention & Control. http://www.goccp.org/msac/crime-statistics.php. Retrieved 2008-06-12.
- ↑ "Hospitals by County – Prince George's County". http://www.hshsl.umaryland.edu/consumer/resources/hospitals.html#prince. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ↑ Fort Washington Medical Center. Official website. URL retrieved on February 11, 2007.
- ↑ Melissa J. Brachfeld (2007-12-19). "Preliminary work on ICC gets under way". The Gazette. http://www.gazette.net/stories/121907/olnenew205950_32357.shtml. Retrieved 2008-08-29.
- ↑ Palmer, Chris (December 17, 2008). ""What's the hoops hotbed of the US right now? Chicago? No. LA? Nope. NYC? Sorry. Welcome to Prince George's County, MD"". ESPN. http://sports.espn.go.com/espnmag/story?id=3775073. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ↑ Who Was Who in America, Historical Volume, 1607-1896. Chicago: Marquis Who's Who. 1963.
External links
- Prince George's County Government, official site
- Prince George's County Historical Society
- The Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission
- The Washington Suburban Sanitary Commission
- The Dilemma of the Black Middle Class, includes analysis of the county.
- The Barbershop, live Internet podcast for Prince George’s County social issues
- Prince Georgians Care site, for and about county residents
- P.G. County by Connie Briscoe, a novel set in Prince George's County
- Crimes in Maryland
- Prince George's County: Looking at the Past, Planning for the Future, a look at the history of development in Prince George's County
- Prince George’s County crime maps
- Prince George's County Memorial Library System
 |
Montgomery County | Howard County |  |
|
| District of Columbia | Anne Arundel County | |||
| Fairfax County, Virginia and City of Alexandria, Virginia | Charles County | Calvert County |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
